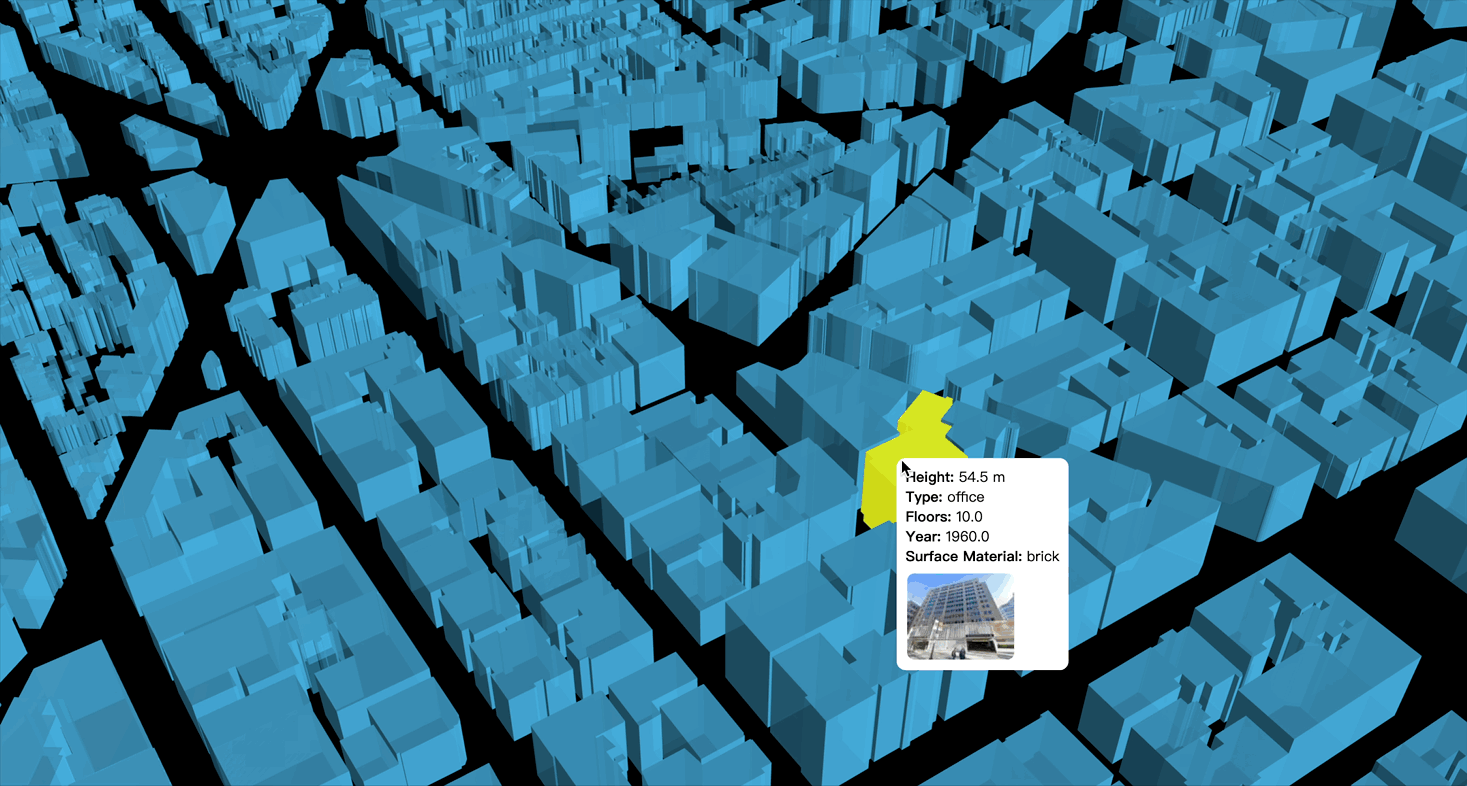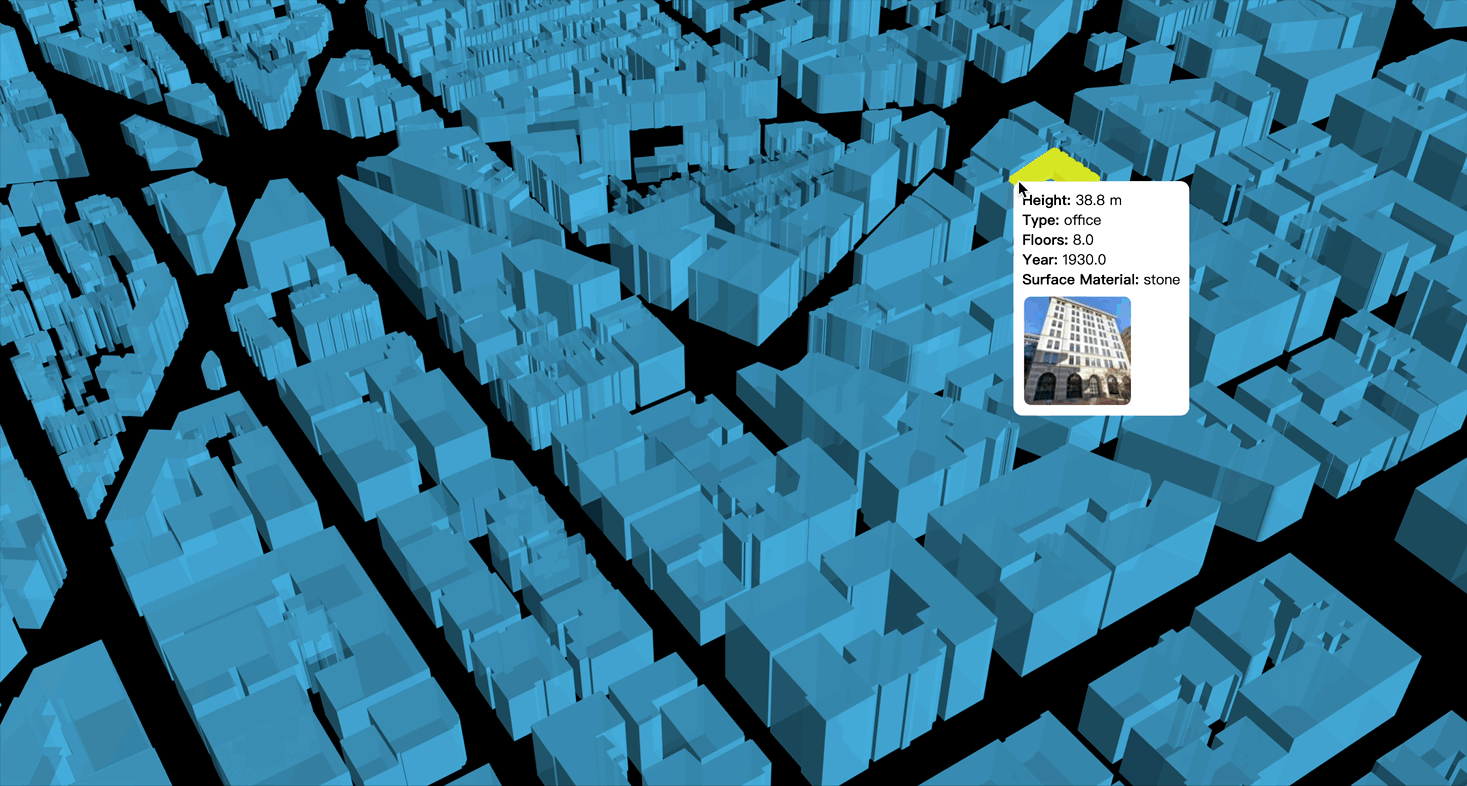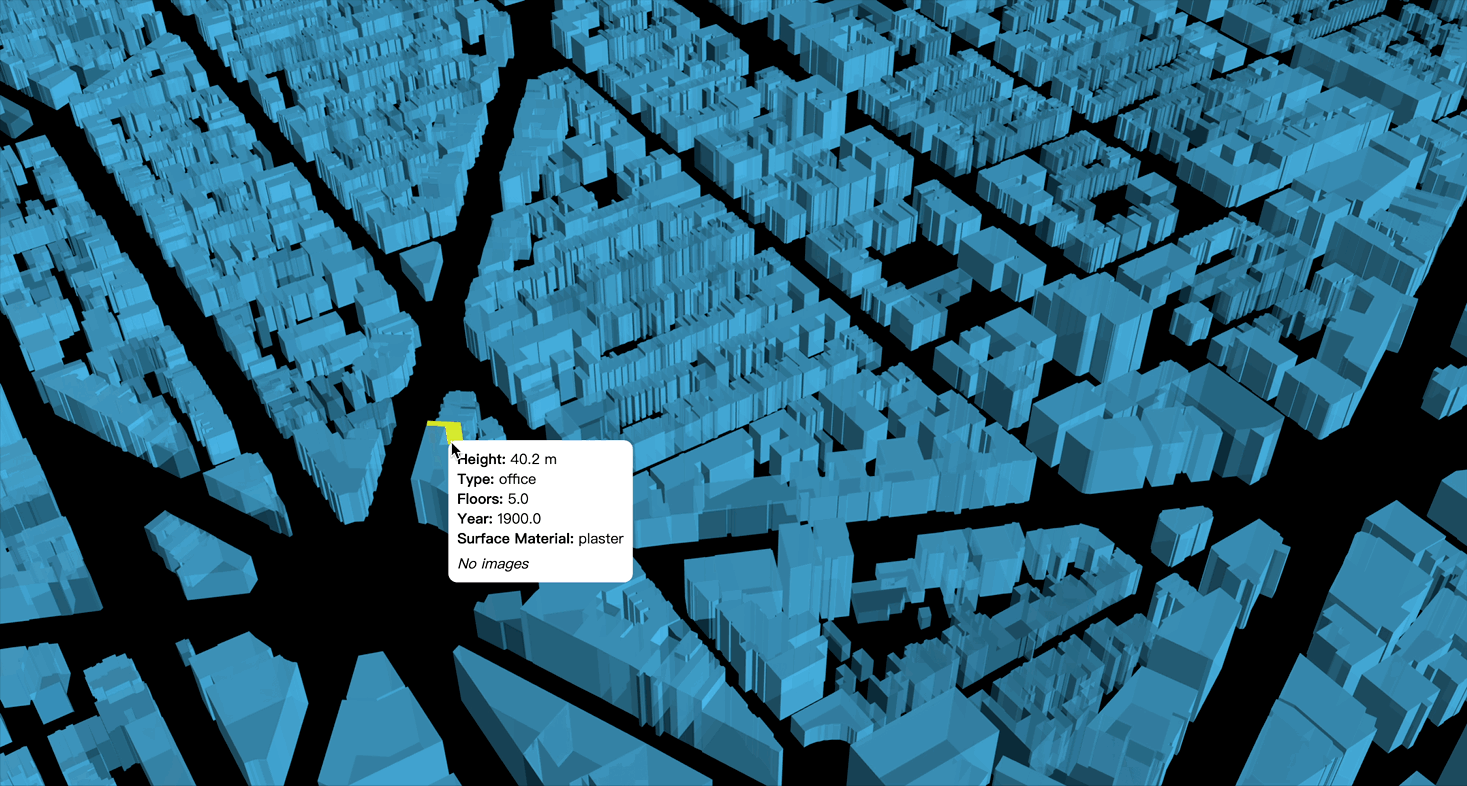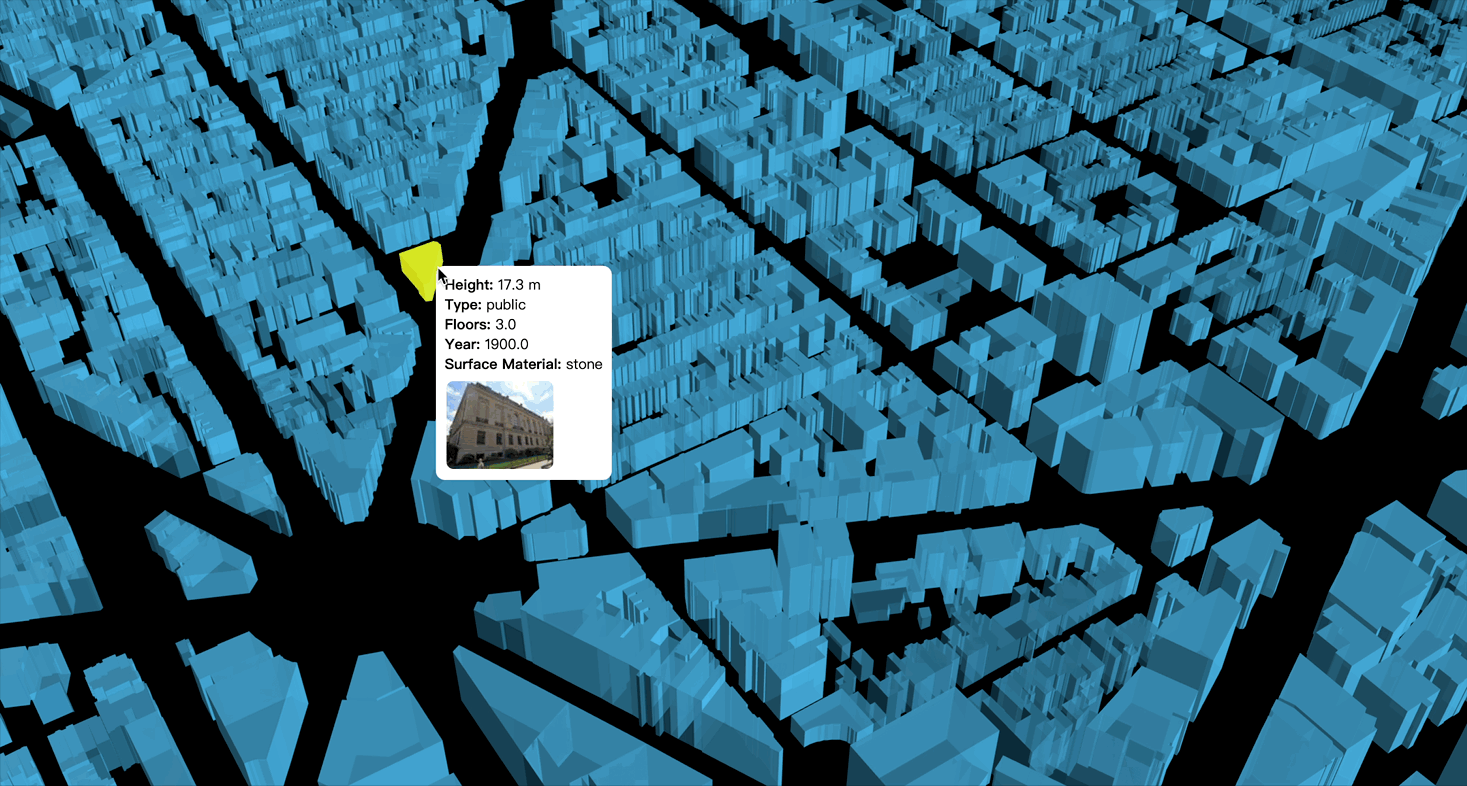
Paper: OpenFACADES: An open framework for architectural caption and attribute data enrichment via street view imagery
Abstract
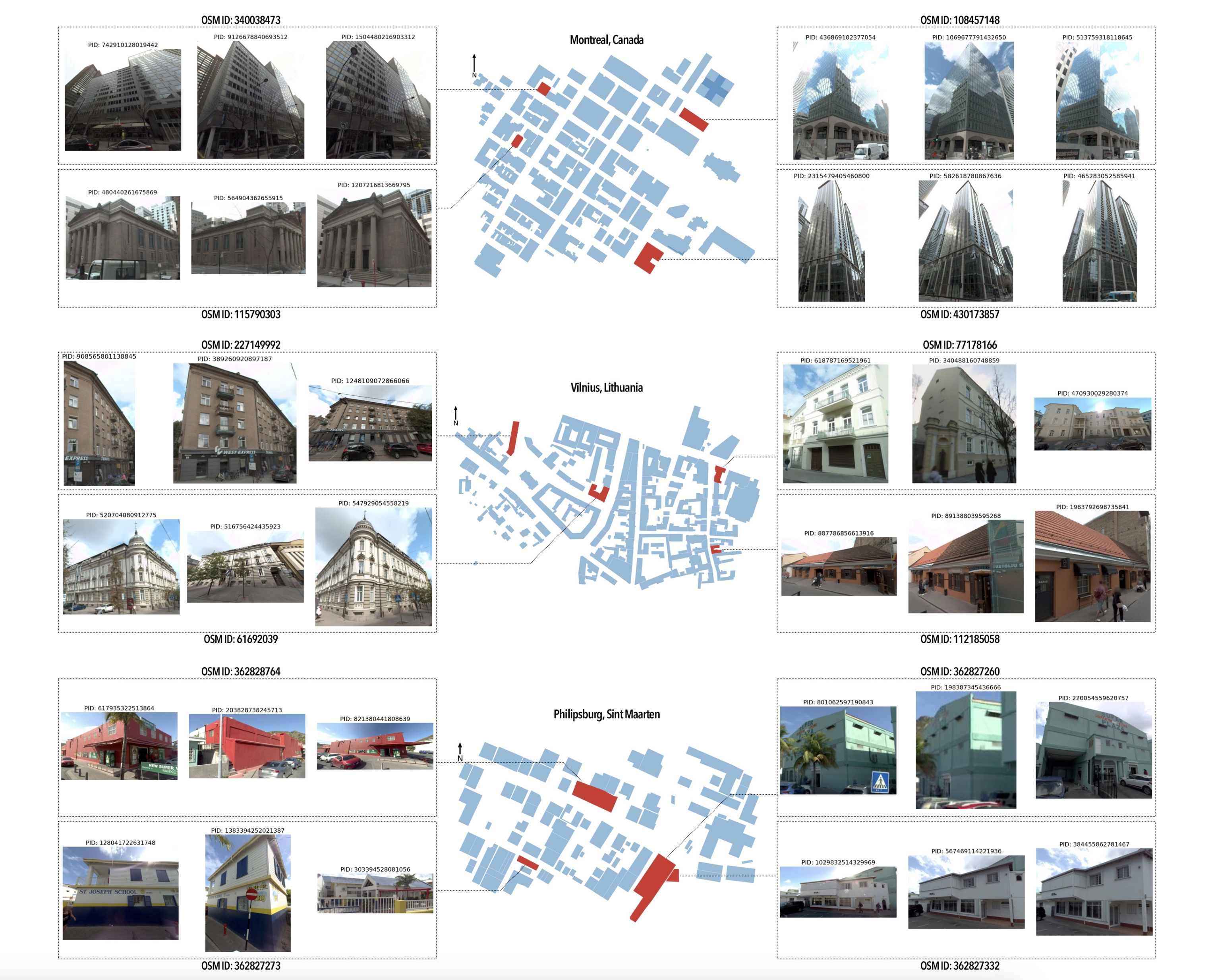
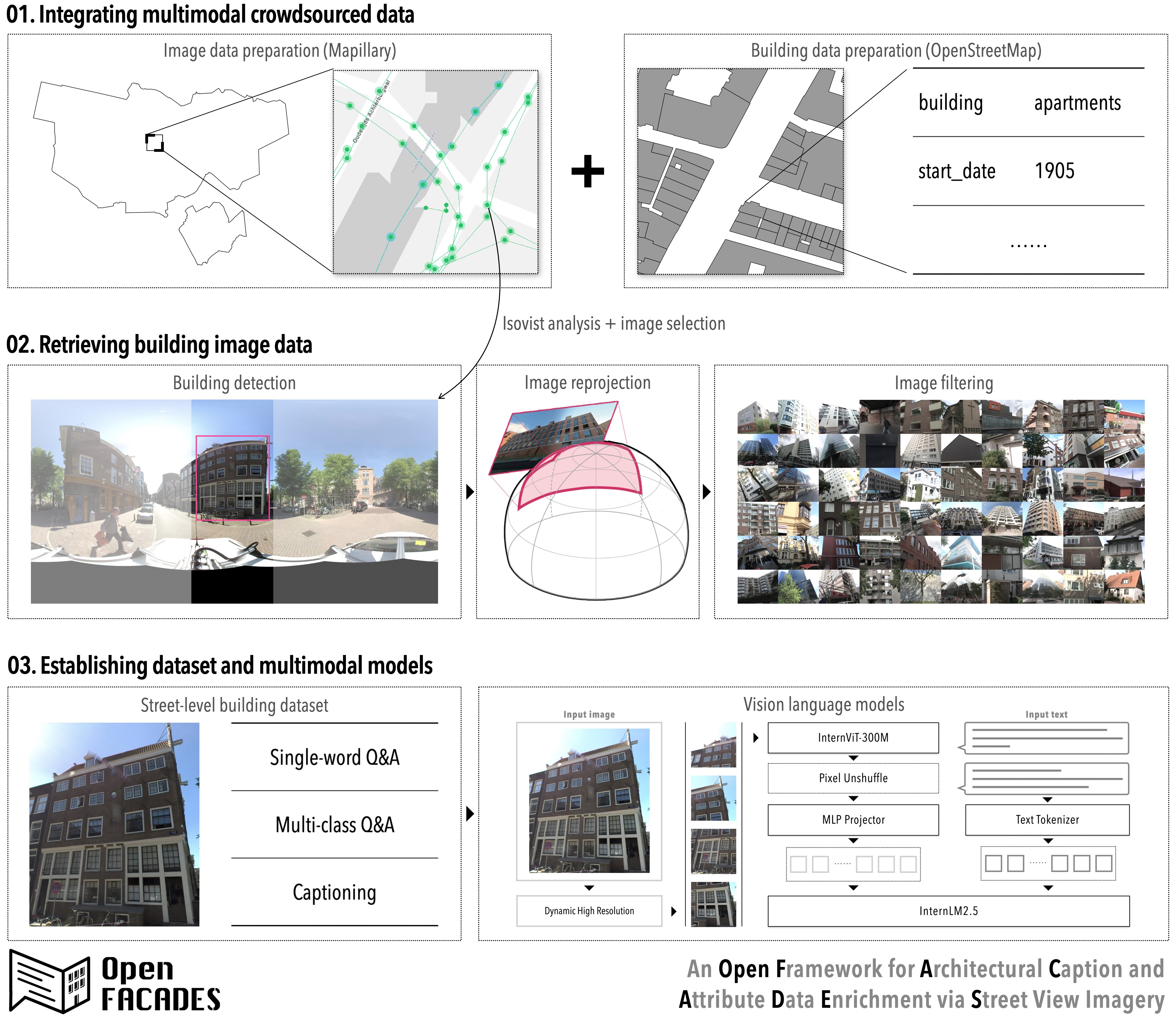

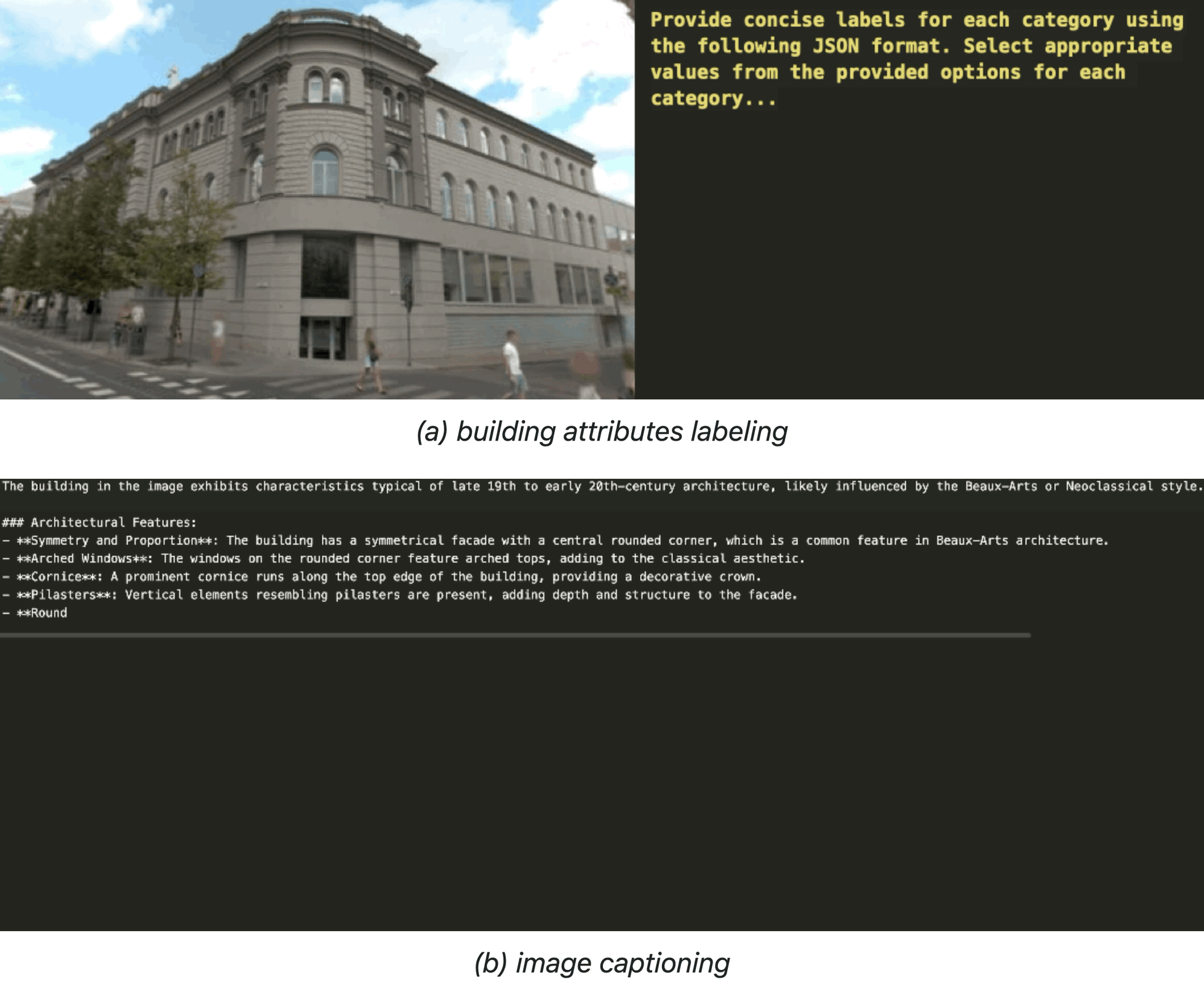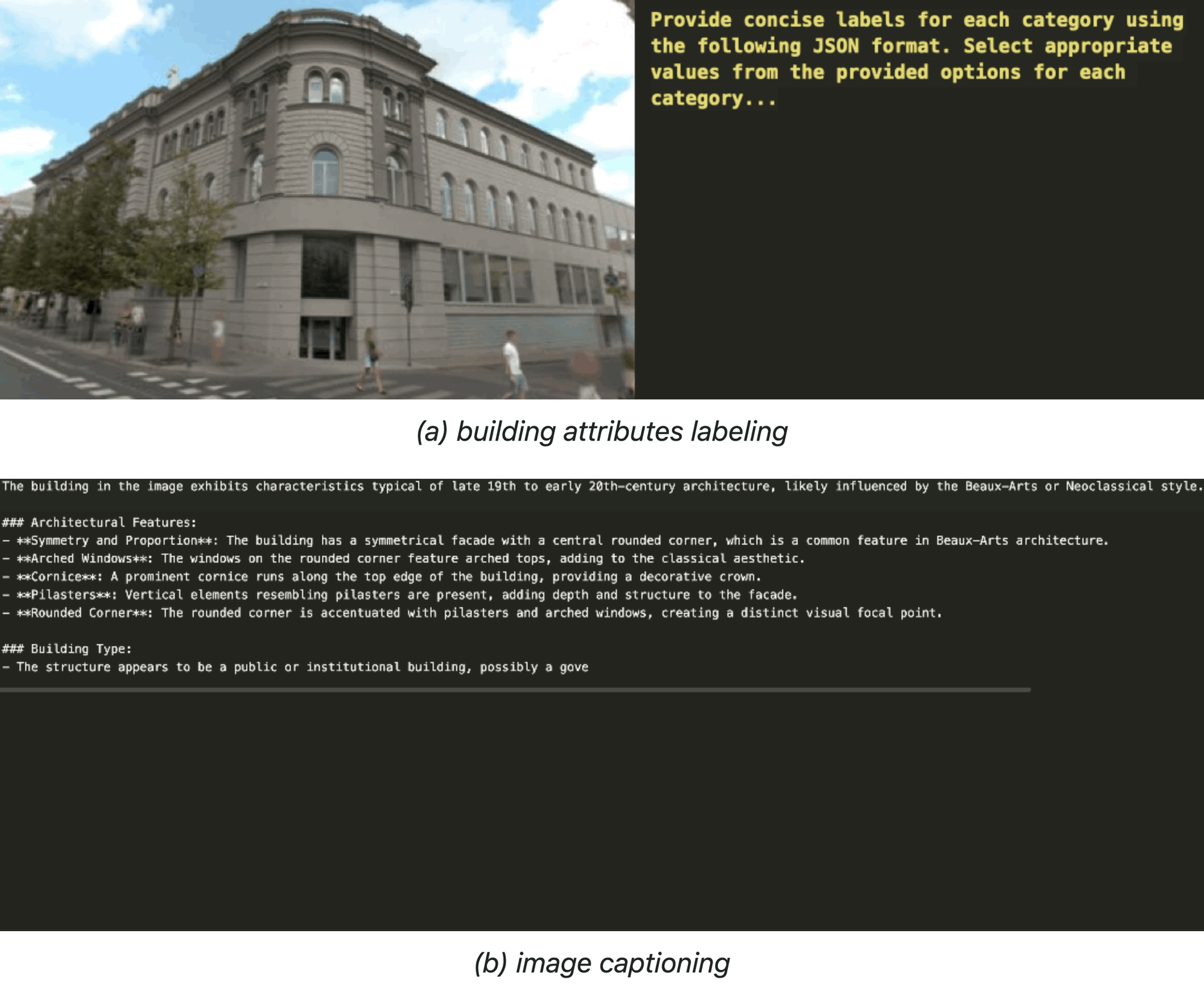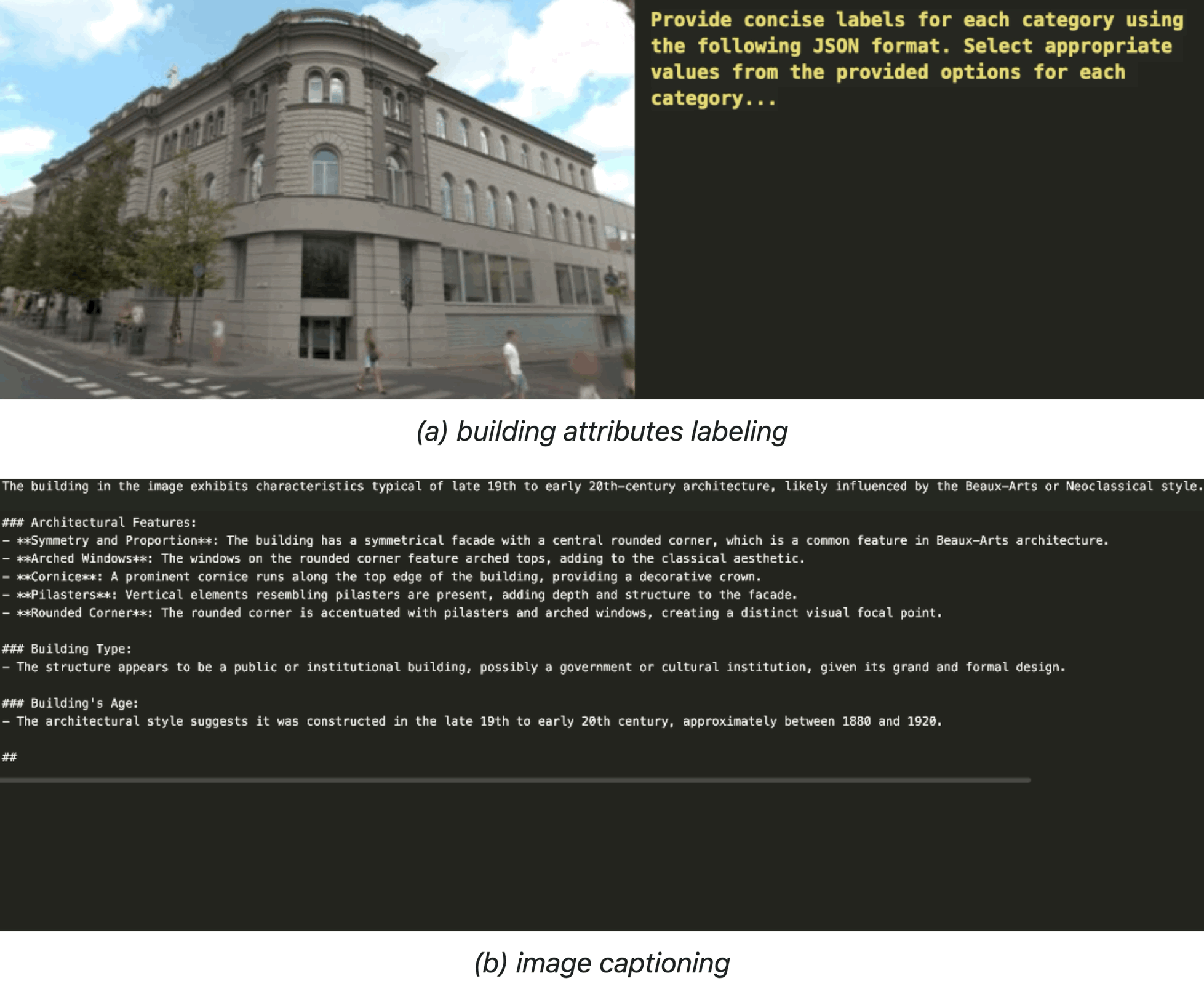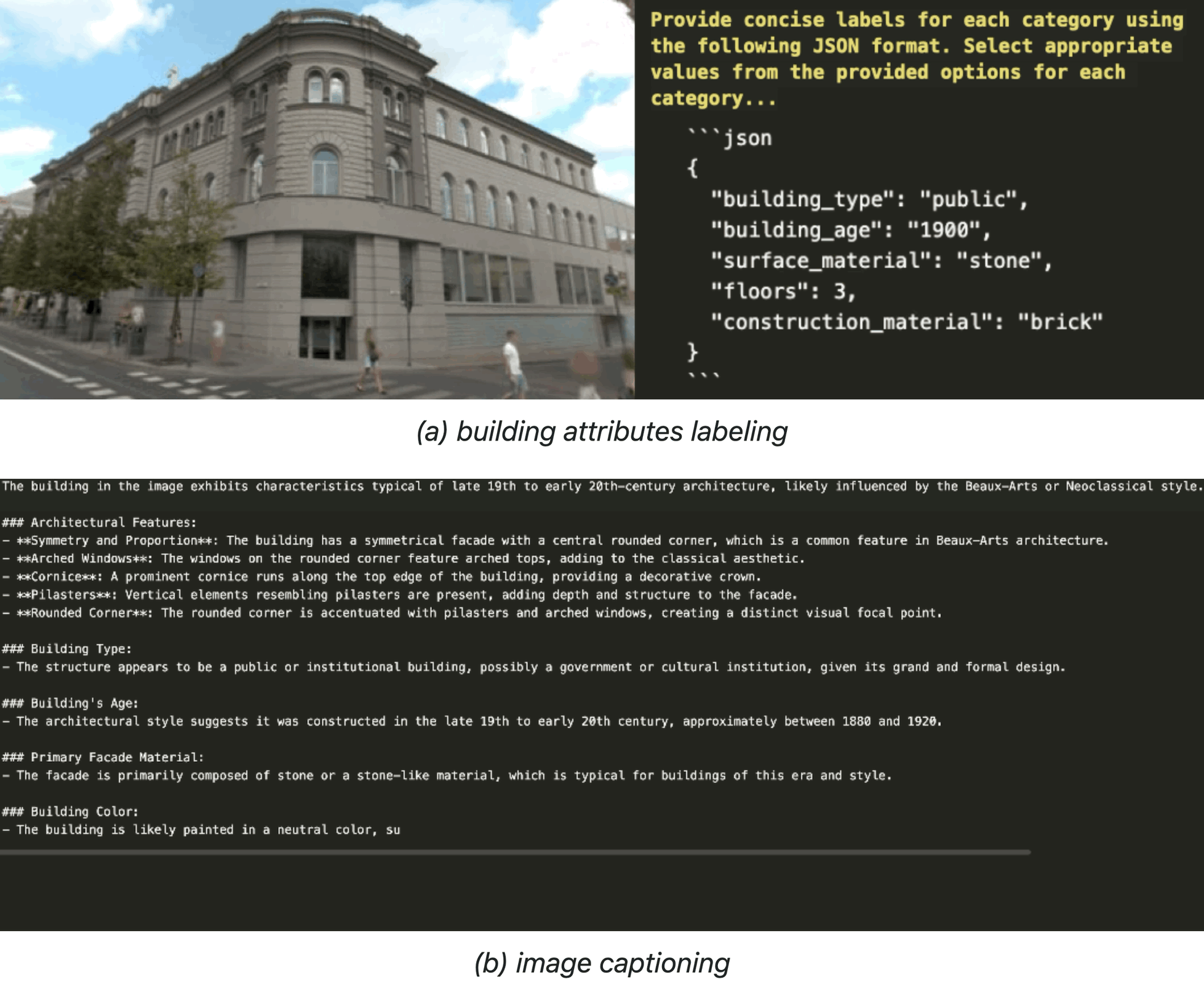
Related Publications
Related Posts

Talk: Climate Change AI Discussion Seminar: Multimodal AI Approaches for Urban Microclimate Prediction and Building Analysis
Attended the October event in CCAI's Discussion Seminar Series. I presented my research on *Evaluating human perception of building exteriors using street view imagery* together with my colleagues Kunihiko Fujiwara and Binyu Lei. The presentation was followed by an interactive discussion in breakout rooms focused on translating this data into meaningful insights.
Read More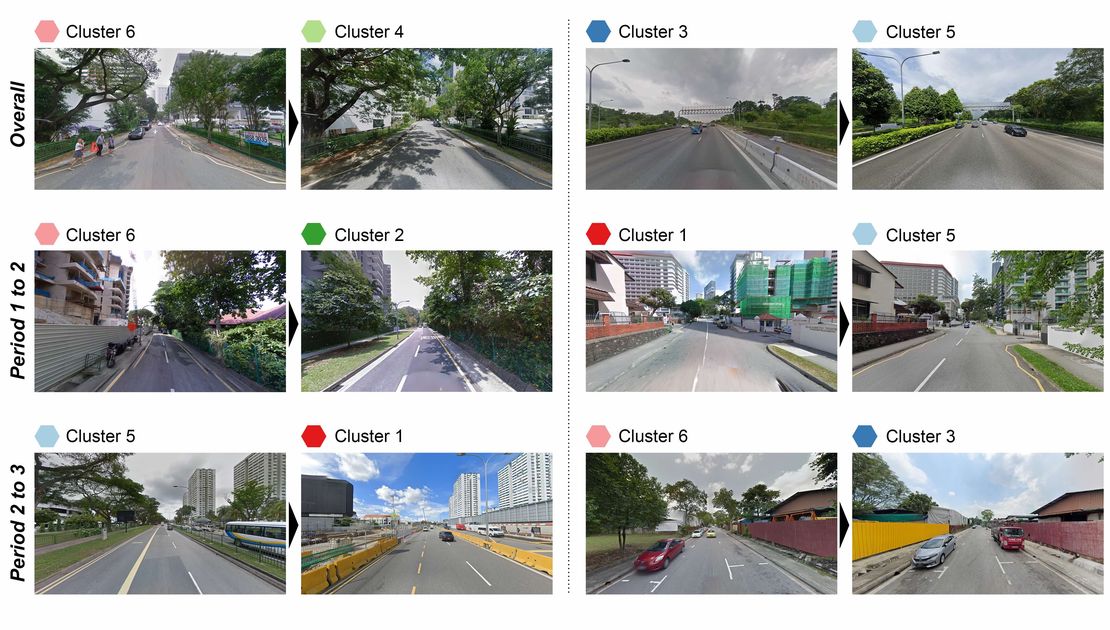
Paper: Revealing spatio-temporal evolution of urban visual environments with street view imagery
This study presents an embedding-driven clustering approach that combines physical and perceptual attributes to analyze the spatial structure and spatio-temporal evolution of urban visual environments. Using Singapore as a case study, it leverages street view imagery and graph neural networks to classify streetscapes into six clusters, revealing changes over the past decade. The findings provide insights into urban visual dynamics, supporting planning and landscape improvement.
Read More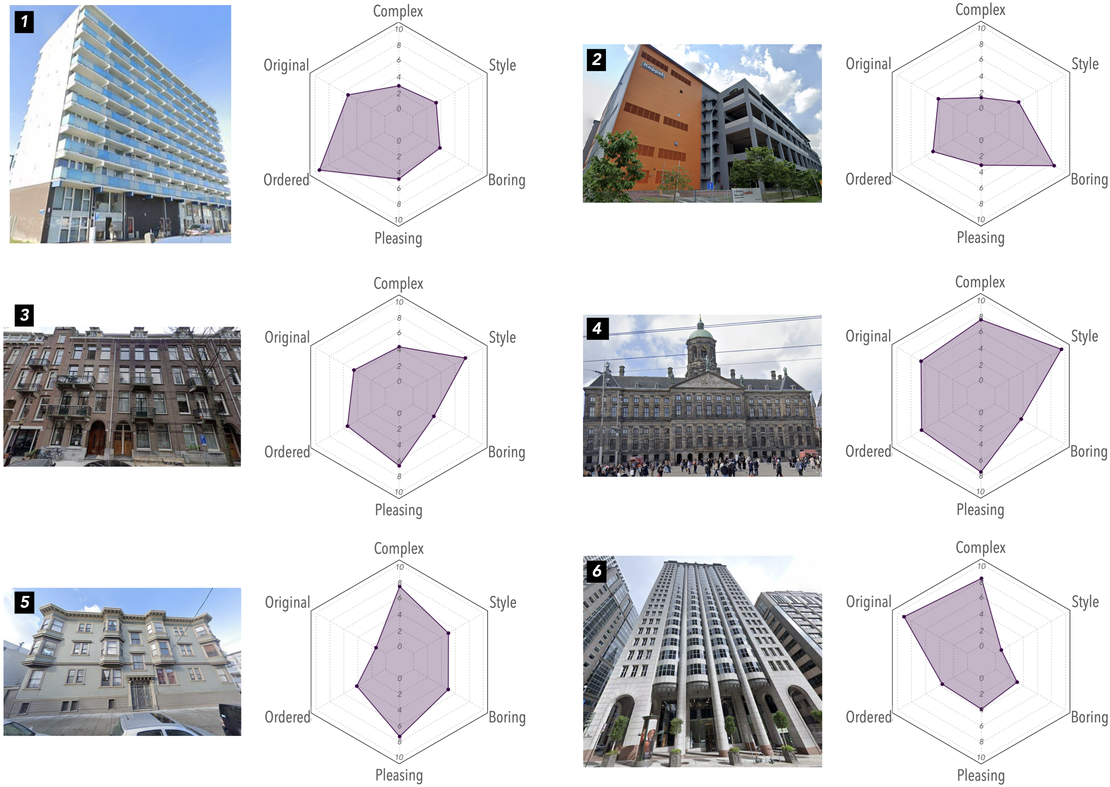
Paper: Evaluating human perception of building exteriors using street view imagery
This study explores how building appearances shape urban perception, using machine learning and survey data to analyze human responses to over 250,000 building images from Singapore, San Francisco, and Amsterdam. Findings reveal how architectural styles influence streetscape perceptions, offering insights for architects and city planners.
Read More